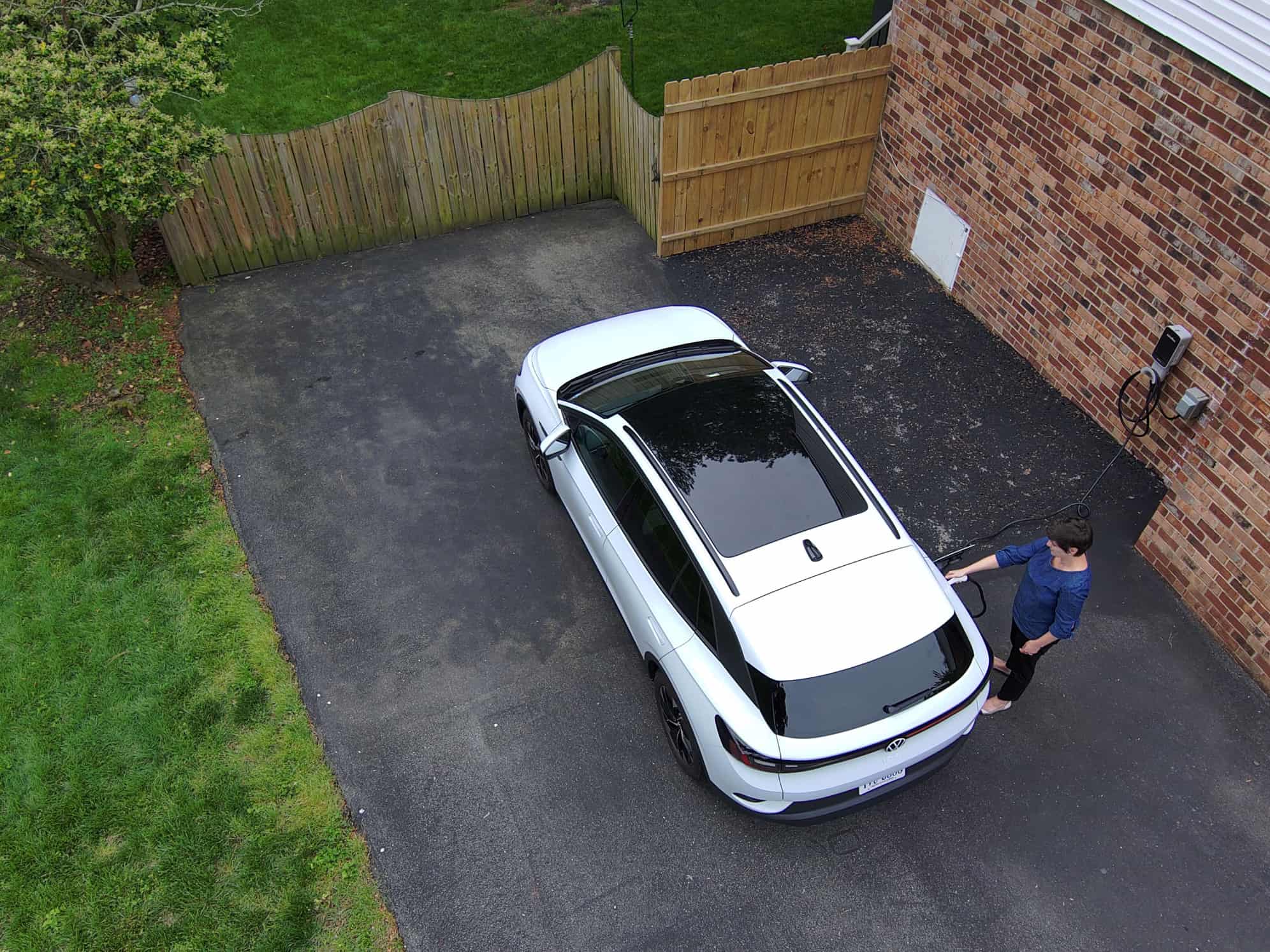
How to Charge an EV at Home
You can charge your EV on the go and at charging stations, but 80% of electric vehicle charging happens at home. How does it work, what are your options, and how can you get the most out of it? Here’s everything you need to know:
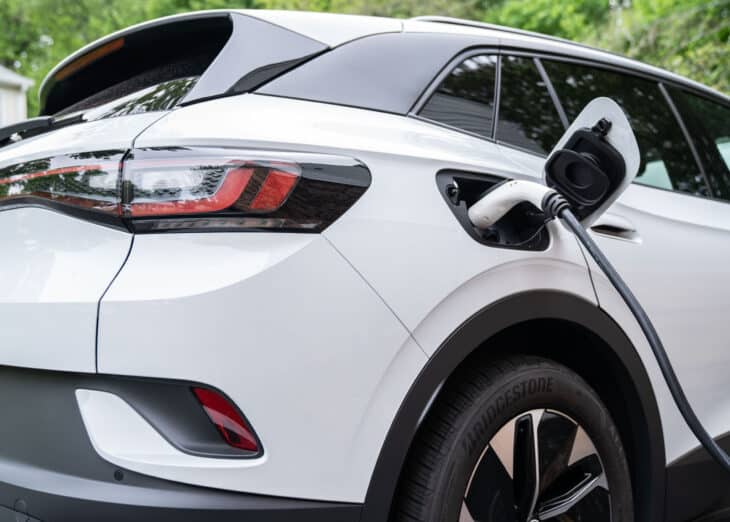

What is EV Charging?
Ninety percent of Americans travel by car and spend an average of 101 minutes a day in their vehicles. It should be no surprise, then, that it is estimated there are 150,000 gas stations across the United States. As we quickly shift to driving electric vehicles, many are shifting their mindsets to ensure they have enough electricity in their batteries before setting out on the road. While more public charging stations are popping up across America, it is estimated that 80% of charging happens at home. This is prompting more EV owners to ask questions like: “How can I charge my EV at home?“
What are the basics of EV charging, and how does it work? Regardless if you are a new EV owner or thinking about buying an EV in the future, below are a few things you should know about how EV charging at home and on the go works for your new vehicle.
What Is An EV Charger?
Electric vehicles require an EV charger to keep their batteries full just like any electronic device in your home. But unlike traditional plugs used for home electronics, EV chargers come in a range of solutions – some unique by manufacturer. The charging cord connects electricity from your home to the charge port in your car much like a hose would connect gasoline from the pump to your tank.
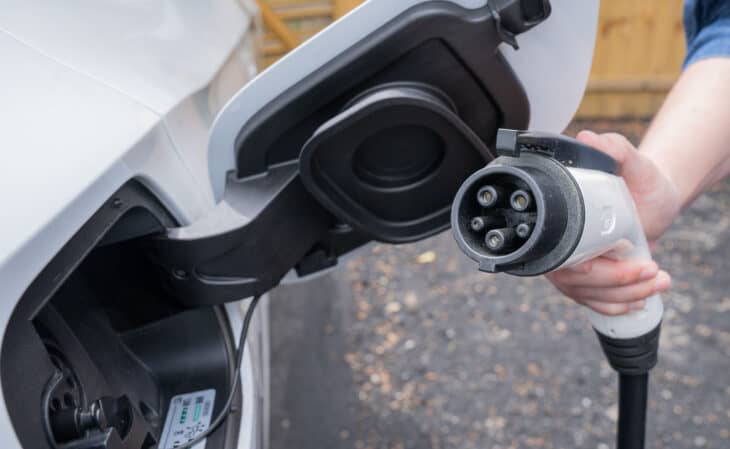

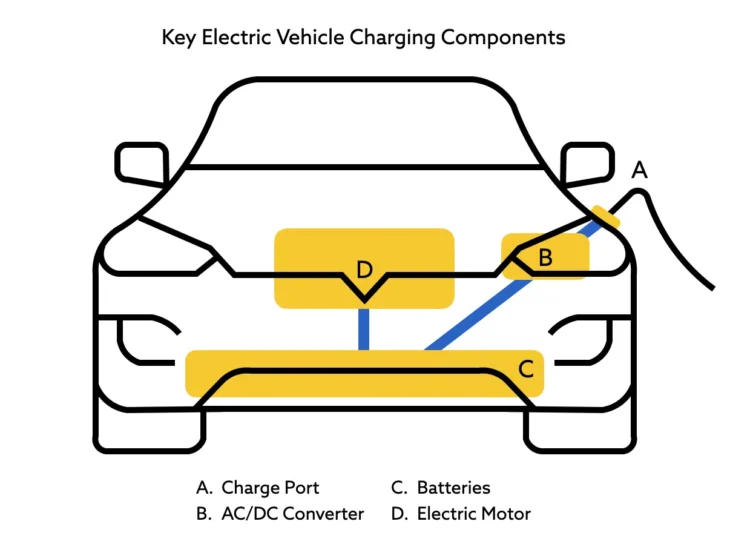
How Does a Home EV Charger Work?
Most electric vehicles are charged with two-way alternating (or AC) current from a Level 1 or Level 2 charger. Many cars can also be charged with direct (or DC) current from a Fast Charger.
In either case, energy flows through the charge port (item A in the diagram). From here, AC current is converted into DC current by your car’s onboard charger (item B). Current can then flow into the batteries (item C) for future use by your electric motor (item D).
What are the Differences in EV Chargers?
There are three main options for charging electric vehicles in the United States – Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. Conveniently, almost all EVs can leverage any of these options with adapters.

What EV Home Charging Options Do I Have?
Charging an electric vehicle is mainly done at home, but not all home chargers are the same. It’s important to understand the solutions available so you can find a solution that best fits your needs and driving behavior. Here at Dominion Energy Solutions, we install EV chargers for homes.
Level 1 Charging
Every electric vehicle is sold with a Level 1 charging cable. These cables can be plugged into any standard 120V outlet in your home or garage. The energy transfer is slow, and it can take upwards of 20 hours to fully charge your batteries.
Level 2 Charging
Level 2 chargers use a 240V outlet shaped like the one used by clothes dryers or ovens. These chargers are typically purchased separately and mounted on the wall where you plan to charge your car; however, some EV car manufacturers offer portable Level 2 chargers. Regardless if the hardware is intended to be portable or mounted in a fixed position, it is recommended you hire a professional to install the 240V outlet that every Level 2 charger requires.
The benefit of purchasing a Level 2 charger is time savings; time to fully charge your car can go from 20+ hours with a Level 1 charger to somewhere between 4-12 hours depending on your vehicle.
DC Fast Charging
Homes are powered by AC current, which means DC Fast Charging (or DCFC) is only available on the go at charging stations. Sometimes referred to as Level 3 chargers, these charging stations send 480 volts of direct current (DC) to your car resulting in much faster charging times. Many cars can be fully charged in 30 minutes.
Which Home EV Charger Is Right For Me?
There are two standards for home charging, Level 1 and Level 2, and all electric cars can be charged with either. The differences between the two can be understood in two ways.
The first way to see the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 charging is how long it will take to fully charge your car. As you can see in the chart below, Level 2 charging is much faster than Level 1 charging.
The second way to see the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 charging is “miles per hour” – but in this case, we don’t mean how far your car will travel per hour but rather how many miles you can store per hour of charging. This is important if you just want to top off with enough power to get where you are going rather than fully charge your batteries. Below outlines the common times it takes for each level of charger to both fully charge your batteries and how many miles you can expect per hour of charge.
| Level | Circuit Voltage | Full Charging Time | Miles Per Hour Charged |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120V | 9-48 Hours | 2-5 Miles/Hour |
| 2 | 240V | 4-12 Hours | 10-20 Miles/Hour |

